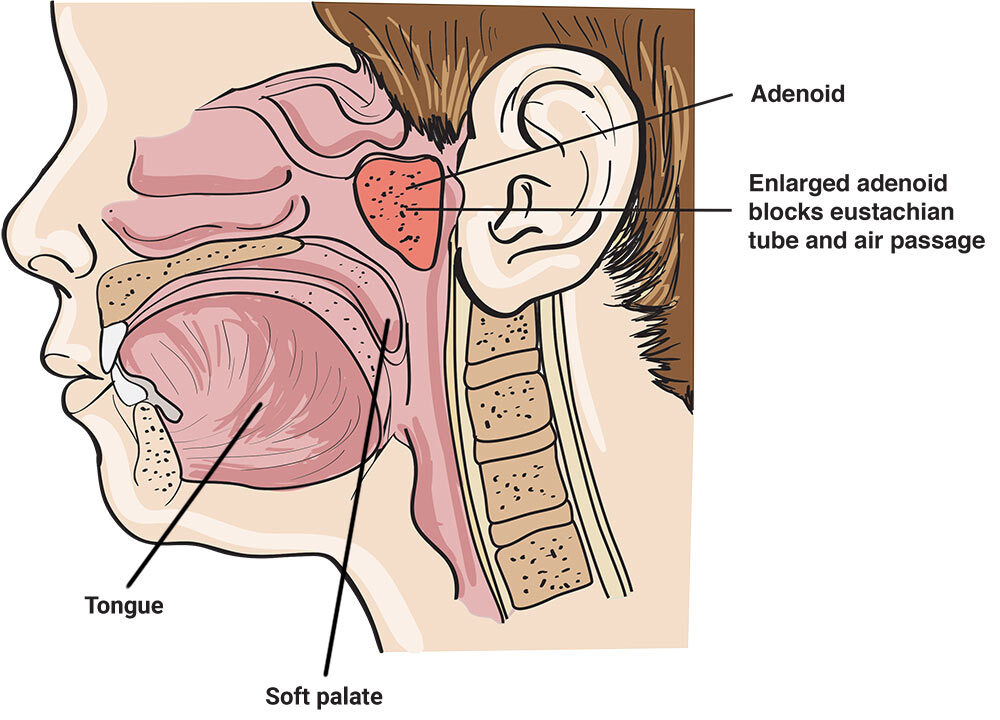
Adenoids are small, soft tissues located at the back of child's nose, behind the roof of their mouth. These structures are part of the immune system and play a crucial role in protecting the body against bacteria and viruses, especially during childhood until child's body finds a way to tackle infections. Since adenoids play such a key role in protection, they often come into contact with germs and then become infected. This condition is known as adenoiditis. Here are some interesting facts about adenoids:
- Adenoids are the largest in children, reaching full size by age 5.
- They naturally shrink by age 7 or 8 and may disappear with adulthood.
- Positioned above the tonsils, adenoids are not visible when looking at the back of the throat.
- Adenoids and tonsils together form a vital part of the immune system.
- They act as a defense against bacteria and viruses entering the body through the nose.
How Big Are Adenoids?
Adenoid size varies, being larger in childhood and naturally shrinking with age—an average adenoid measures 6.2 mm, while enlarged adenoids are around 11.6 millimetres. However, enlarged adenoids are caused due to various reasons, such as bacterial and viral infections.
What Are Adenoids Made Of?
Behind their unassuming appearance, adenoids are made of lymphoid tissue. This tissue contains cells (white blood cells) that actively contribute to fighting bacteria and viruses by producing antibodies.
Common Conditions That Can Affect Adenoids
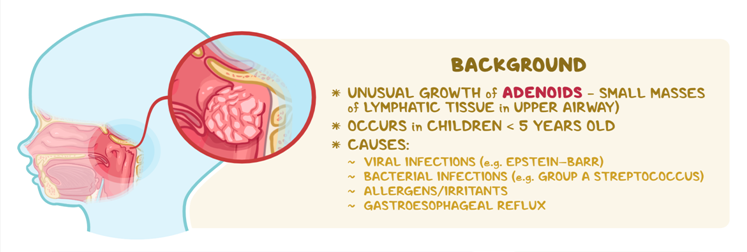
Although adenoids work hard to filter germs from child's body, they can sometimes be overrun by bacteria, causing enlarged or infections. Thus, they become inflamed and enlarged. Here are a few enlarged adenoids causes:
- Ear infections can happen often.
- Upper respiratory infections can occur frequently.
- Nosebleeds that keep coming back.
- Frequently dealing with enlarged adenoids caused by allergies to substances found in air or food.
Common Signs or Symptoms of Enlarged Adenoids
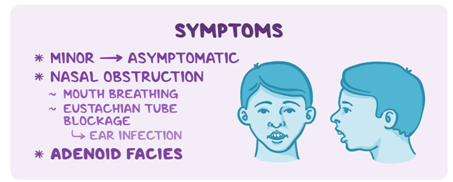
Recognizing the signs of enlarged adenoid symptoms is very important. Enlarged adenoid symptoms may include:
- Congested or blocked nasal passages.
- Breathing difficulties through the nose.
- Dry mouth and cracked lips due to breathing issues.
- Glue ear is a condition where fluid buildup in the middle ear causes hearing problems.
- Sleep disturbances and difficulties.
- Snoring during sleep.
- Persistent sore throat.
- Challenges with swallowing.
- Swollen neck glands.
- Sleep apnea, which means pauses in breathing during sleep.
Diagnosis
The doctor will inquire about child's symptoms and conduct a physical examination.
Imaging Tests- X-rays,CT scans7, or MRI scans are utilized to gain a detailed view of child's nasal passages, sinuses, and adenoids.
Sleep Studies-If enlarged adenoids contribute to obstructive sleep apnea or snoring, a sleep study may be recommended to monitor and assess child's sleep patterns. During this study, child sleeps overnight at a facility while breathing and brain activity are monitored with electrodes.
Nasal Endoscopy-The doctor directly views the adenoids using a unique mirror and a flexible telescope (endoscope) inserted through the nose. This helps determine inflamed, red, or enlarged adenoids.
Bacteria Throat Culture Test- A throat culture test helps to figure out if an infection is causing the enlarged adenoids by identifying the specific bacteria or organisms.
If the results are positive, the doctor will decide on the enlarged adenoid treatment.
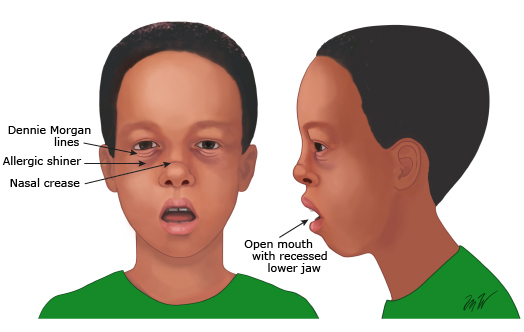
What are the adenoid facies?
Adenoids facies refers to the atypical appearance of facial features, and can result from persistent adenoids hypertrophy. Commonly, adenoid facies is known as “long face syndrome”, and is characterized by a long, lean face with an open mouth. With adenoids facies, individuals typically present with increased mouth breathing, an arched palate, underdeveloped upper jaw bones, a short upper lip, elevated nostrils, and dental crowding of the front teeth. It most commonly occurs in children and often presents with chronic nasal obstruction.
What are the side effects of having your adenoids removed?
Adenoids removal is generally not considered to be a high-risk surgery. However, the most common side effects are nose or mouth bleeding, bad breath, sore throat, fever, nausea, and vomiting. Other, less common, side effects include problems with swallowing, ear pain, or permanent changes in vocal quality. If an individual presents with persisting side effects, medical attention may be required. Also after removal of adenoids the first line of defense of body is gone so the individual becomes more prone to recurrent respiratory infections
Conventional treatment of enlarged Adenoids
Typically, adenoiditis will resolve within a week. In case of presumed large adenoids with no signs of infection, doctor may consider a trial of nasal steroid spray or antihistamines. if symptoms don’t get better, despite medical management, your doctor may refer you to an ENT surgeon. They may discuss the option of surgical removal of adenoids (Adenoidectomy). But we would suggest to avoid surgical removal as Homoeopathic medicines can resolve it without getting any surgery done.
How homoeopathy helps in enlarged Adenoids?
Homeopathy has great scope to treat adenoid conditions in children like recurrent adenoid infection, and allergic conditions and prevent children from adenoid faces. Proper homeopathy treatment under the guidance of a homeopathy physician helps to preserve adenoids which are part of immune system and reduce the tendency of the adenoid face. Depending on symptoms, the history of a patient, and causative factors for adenoid infection, homeopathy has acute and chronic remedies.