The immune system serves as the body's defense against infections, comprising a complex network of cells, chemicals, tissues, and organs. It plays a crucial role in identifying and combating invaders such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and abnormal cells like cancer cells. By generating an immune response, it helps the body resist and fight off these threats.
When harmful microorganisms enter the body, it triggers the production of white blood cells, which play a key role in identifying and attacking the invading germs. These white blood cells also produce antibodies, which are specialized proteins that target and neutralize disease-causing germs. Additionally, white blood cells contribute to various immune responses and have the ability to remember previous infections they have encountered.
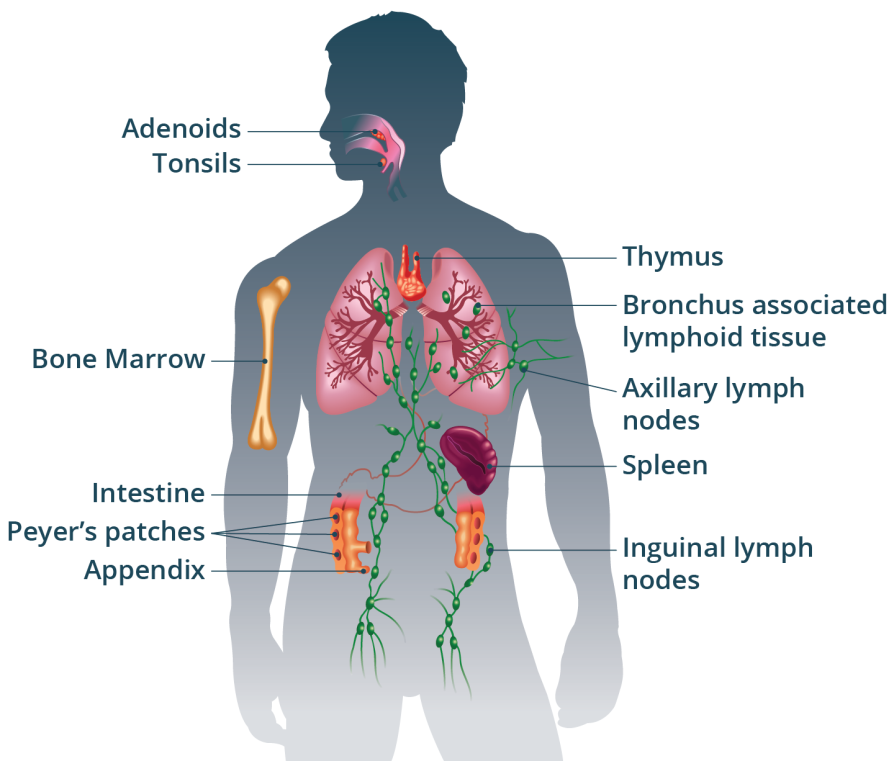
The parts of immune system
The immune system is composed of various components throughout the body, each contributing to the recognition of pathogens, communication between different body parts, and the coordinated effort to combat infections. These components include –
- The skin
- Bone marrow
- Thymus
- Lymphatic system
- Lymph nodes
- Spleen
- Mucous membranes
Each part plays a distinct role in protecting the body from illness and maintaining overall health.
Working of immune system
Each component of the immune system functions uniquely:
- The skin acts as a primary barrier, preventing germs from entering the body.
- Bone marrow plays a crucial role in producing immune cells.
-The thymus gland - Located in the upper chest, where certain immune cells mature.
- The lymphatic system consists of small vessels that enable immune cells to move between tissues and the bloodstream. It contains lymphocytes (predominantly T cells and B cells) that detect and combat bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. These cells circulate in lymph, a fluid with a milky appearance.
- Lymph nodes are small clusters of tissue found in the groin, armpits, neck, and elsewhere, facilitating communication within the lymphatic system. They may swell during immune responses.
-Spleen - Positioned under the ribs on the left side, itfilters information from the blood.
- Mucous membranes, such as those lining the mouth and nose, trap germs and enable immune cells to capture and eliminate them.
The immune conditions
There are various immune-related conditions that can arise from either an underactive or overactive immune system.
An overactive immune system can lead to conditions like allergies and autoimmune diseases:
- Allergies involve the immune system reacting to substances that are typically harmless, such as pollen or certain foods.
- Autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis, occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the body.
Conversely, an underactive immune system, known as immunodeficiency, increases the susceptibility to infections. In immunodeficiency disorders, the body's ability to combat infections is compromised:
- Primary immunodeficiencies (PID) are conditions one is born with, affecting the immune system's ability to function properly.
- Secondary immunodeficiencies can develop due to medical treatments or other diseases, further weakening the immune response against infections
The common symptoms of immune conditions
If you have an immunodeficiency, you may have some of the following symptoms:
- poor growth (children)
- recurrent or severe infections(pneumonia, sinusitis, skin abscesses, ear infections, meningitis)
- infections with unusual germs
- chronic diarrhea
- oral thrush
- severe eczema
If you have allergies, you may have some of the following symptoms:
- swelling of the lips, tongue, face and eyes
- difficulty breathing
- Frequent cold cough
- Recurrent tonsillitis
- a rash with hives
- abdominal pain and vomiting
If you have an autoimmune condition, the symptoms will vary depending on what part or your body is affected.
A weak immune system can lead to constant colds, fatigue and infections.
The immune system protects you from illness and infection. It is a complex network of cells and organs – including your skin and white blood cells – which work together as a first and second line of defence.
Unfortunately, sometimes our immune systems don’t work as well as expected, which can make you more susceptible to viruses and infections.
What is poor immunity?
Poor immunity occurs when your body's defense system, designed to protect against illnesses and infections, is not functioning optimally. This weakened state can manifest as increased fatigue, feeling generally unwell, and experiencing digestive issues more frequently. A compromised immune system may result in recurring colds, persistent fatigue, and heightened susceptibility to infections.
The immune system is a sophisticated network comprising cells and organs, such as skin and white blood cells, which collaborate to provide primary and secondary lines of defense against pathogens.
Occasionally, our immune systems may not operate at peak efficiency, leaving us more vulnerable to viruses and infections.
Causes of poor immunity
You can have an inefficient immune system from birth, or it can weaken as you get older. Aging can reduce its effectiveness. Lifestyle factors that can also weaken your immune system include:
- Poor sleep
- Overexertion
- Stress
- Bad nutrition
Several medical factors can also harm your immune system:
- Immunodeficiency disorders (primary or secondary)
- Radiation and cancer treatments
- Exposure to harmful chemicals
- Conditions like multiple sclerosis, cancer, Crohn's disease, or chronic fatigue syndrome
- Certain medications like antibiotics and steroids
Symptoms of a Poor immune system
Certain signs can indicate if your immune system is weak. Here are five of them:
1. Frequent Cold Symptoms: It's normal to get a cold occasionally, but if you have persistent colds or they last longer than usual (more than 7-10 days), it could indicate a compromised immune system that struggles to fight off infections.
2. Regular Ear Infections: Developing more than four ear infections a year might suggest weakened immunity, similar to frequent colds.
3. Persistent Fatigue: Feeling constantly tired beyond typical daily fatigue could be a sign of an immune system that isn't functioning properly. Your body may be expending extra energy to combat infections and bacteria.
4. High Stress Levels: Long-term stress can weaken the immune system by reducing the levels of lymphocytes, the white blood cells crucial for fighting infections. This makes you more susceptible to illnesses.
5. Digestive Issues: Prolonged diarrhea (lasting two to four weeks) or persistent constipation can indicate immune system dysfunction affecting the digestive tract.
These symptoms may also be caused by other health conditions, so it's important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Are you at risk of a weakened immune system?
We should all keep a close eye on our immune system health and support it by living a healthy and active lifestyle. If you have a family history of primary immunodeficiency disorders, for example, then your risk of having a primary disorder (or passing one on to your children) is higher. If you are falling sick frequently and need support of antibiotics, anti- allergic and steroidal medicines in short intervals and episodes are increasing that means your immunity is low.
Anything that threatens your immune system could potentially lead to secondary immunodeficiency disorder.
Helping immune system
You may be able to support your immune system better by making a few small changes. Simple immune-supporting lifestyle tips:
- Reduce stress:Chronic stress can also lead to elevated levels of cortisol, a hormone that suppresses the immune system.
- Get a good night’s sleep: During sleep, the body produces and releases cytokines, which are proteins that help regulate immune responses.
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system and make it less effective in fighting off infections. .
- Do not smoke: Smoking can suppress the production of antibodies and impair the activity of immune cells, such as natural killer cells and T cells.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise is known to reduce stress levels by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood-boosting chemicals.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Not only is maintaining a healthy weight important for better overall health, there is evidence to suggest that obesity is associated with an impaired immune response.
- Eat a balanced diet:. Ensure your diet incorporates some, or all, of the vitamins and minerals, that are primarily associated with good immune system health (Vitamin A, Vitamin C, zinc, Selenium and Vitamin D).
- Homoeopathic Tretament : Homeopathy is believed to boost immunity by stimulating the body's self-regulating mechanisms. Remedies are chosen based on individual symptoms and constitution, aiming to restore balance and strengthen the body's natural defenses. This approach is thought to enhance overall health and resilience by addressing underlying imbalances that may weaken immunity. Homoeopathic treatments support immune function without suppressing symptoms, promoting long-term wellness. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims remains limited and varies in its conclusions.
How Homoeopathy works in boosting your immunity
Homeopathy, in contrast to antibiotics, does not neutralize an infection instead, it strengthens the body's defenses against illness and disease.
- The contemporary homeopathic philosophy emphasizes systemic cleansing, which weakens the body's defenses. Therefore, it eliminates poisoning or toxicity from the lymph nodes, liver, spleen, lymphocytes, and bone marrow, all of which are crucial components of the immune defense system.
- Since the mildly sweet tablets, powders, and liquids in homeopathy are simple to administer and take, they are more delicious than many conventional medications.
- Any issue connected to a weakened immune system or immunological response responds well to homeopathy.
- After a few days, the patient receiving homeopathic treatment regains appetite, aiding in weight gain.
- Opportunistic illnesses linked to weakened immunity can be controlled with homeopathy.
- After a few months of frequent use, homeopathy reduces the viral burden.

